Guide to Melasma: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention

Medically reviewed by Joni Gunzburger, MSN, FNP-C on November 10, 2022
If you’ve started to notice patches of darker skin (also known as hyperpigmentation) across your face, you may have melasma. It’s a skin condition that causes uneven skin tone and dark patches across the cheeks, forehead, nose, and chin. While it’s not harmful, it can affect your self-esteem.
Luckily, there are different types of melasma treatment to reduce symptoms. Some of these require an in-office procedure (for example, a chemical peel or laser treatment), and limiting your sun exposure may fade the hyperpigmentation of melasma over time. As for topical treatments, the prescription medication hydroquinone is usually dermatologists’ go-to melasma solution.
Of course, the type of treatment depends on which kind of melasma you have. Learn more about how to treat this skin condition below.
Nurx offers prescription treatment for acne, anti aging, melasma, rosacea, and eyelash growth.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a type of skin discoloration that primarily affects women — in fact, 90% of all cases occur in women. Because it frequently happens in pregnant women, it’s also known as the “mask of pregnancy.”
What Are the Clinical Features of Melasma?
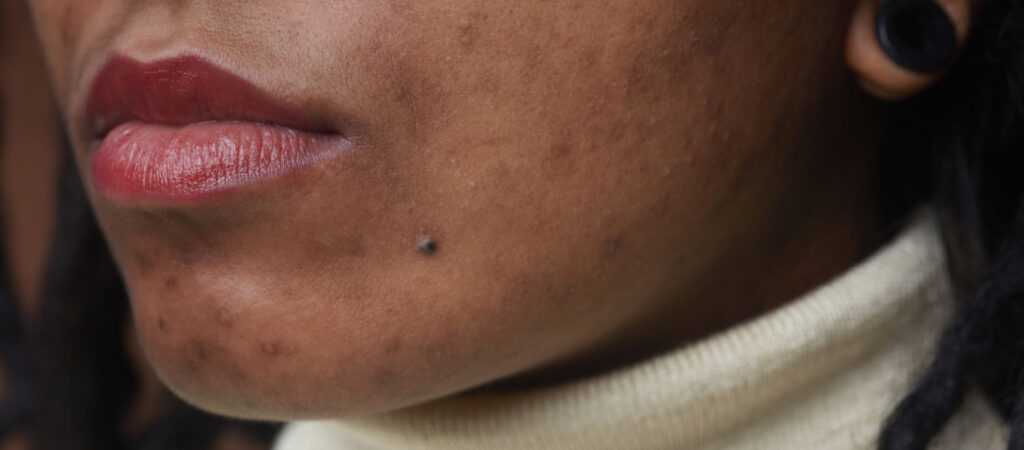
Melasma causes skin discoloration in areas like the chin, cheek, ear, and above the upper lip. These dark patches may look like freckles at first. Melasma is usually symmetrical in that it appears on both sides of the face.
Color can also vary depending on your skin’s pigment. In people with light skin, you’ll likely notice brown dark spots. People with a darker skin tone might see a bluish-gray dark spot instead.
There are three main types of melasma. Epidermal melasma usually means the hyperpigmentation is darker, has a well-defined border, and is very obvious in both visible light and black light. Dermal melasma is deeper in the skin, meaning the spots are lighter, harder to see under a black light, and unfortunately, more treatment-resistant. Finally, mixed melasma is a combination of both of these conditions.
How Are Hyperpigmentation and Melasma Different?
Hyperpigmentation is a broad category for all types of excess pigment in the skin. Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation specifically tied to factors like hormones, genetics, certain medications, and more. However, hyperpigmentation in general can be caused by things other than melasma, including excess sun exposure, inflammation, acne scars and more. Sunspots are another good example of hyperpigmentation
What Makes Someone Prone to Melasma?
Being pregnant is one of the main factors that can contribute to the development of melasma, indicating a link to elevated levels of estrogen and progesterone can trigger melasma lesions. Melasma is just one of several pregnancy skin disorders, however, so it’s important to consult a medical provider to know for sure what skin condition you have.
Other factors that might make you susceptible to melasma include taking certain medications (like birth control or anti-seizure medications), using certain types of makeup or soap, or having hypothyroidism.
Complications of Melasma
While having melasma can be frustrating, the good news is that there aren’t really many complications or side effects to worry about. You won’t notice any skin irritation, pain, or itchiness around melasma dark patches — they’re only a visual condition. Instead, side effects might occur from the different melasma treatment options you try.
What Are the Side Effects of Melasma?
If you’re using a melasma cream to treat your symptoms, you may develop temporary skin irritation, such as dry or scaly skin. If you use these creams for longer than directed, you may also be at risk of a complication called exogenous ochronosis, a type of permanent discoloration.
You can also try an in-office chemical peel or laser skin rejuvenation to treat melasma. Both of these have side effects of skin irritation, swelling, peeling, and redness.
One of the treatments with the least side effects is hydroquinone. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of melanin, which reduces the pigment in your dark spots.
If you’re on birth control and your medical provider thinks it might be contributing to your melasma, they may recommend you switch to a estrogen-free contraceptive instead, such as an IUD or the mini pill.
Treatment for Melasma
There isn’t one best treatment for melasma. Instead, your medical provider will need to take a look at your medical history and symptoms before making a recommendation. Luckily, for many people who develop melasma during pregnancy, it often goes away on its own after you give birth. But if your melasma isn’t linked to pregnancy or doesn’t start to fade, melasma treatment can help.
The main goals of melasma treatment are to decrease the melanin (pigment) your body makes, as well as even out your existing skin tone. There are several ways to achieve this, including medications, creams, and more invasive treatments.
How Long Can It Take to Treat Melasma?
Melasma treatment isn’t immediate. Often, it can take three to 12 months to see results. During that time, you might want to try camouflage makeup to even out your skin tone and mask any brown spots. During that time, if you aren’t progressing, your medical provider may try out a few different treatments until they find the solution that works for your skin type.
What Does the Recovery Process Look Like After Melasma Treatment?
Most melasma treatments aren’t immediate. In the case of a chemical peel or laser treatment, you’ll need anywhere from a few days to a few weeks of rest before swelling and redness go down. Medical providers recommend avoiding working out or sweating, as this can irritate the skin further.
During this time, medical providers recommend you avoid unnecessary sun exposure and use sun protection if you must be in the sun. That’s because too much sun stimulates melanin production in the skin, which can in turn worsen your melasma. You’ll also want to avoid wearing makeup or doing intense skincare routines. — but always remember to moisturize!
When Should You Talk to a Medical Provider About Melasma?
Any time you start seeing changes in your skin, you should consult a medical provider. Only they’ll be able to tell the difference between other types of hyperpigmentation and melasma. They’ll also be able to verify that your darker skin tones aren’t actually skin cancer or another skin condition.
What Permanent Melasma Removal Options Are There?
There aren’t really any permanent treatments for melasma out there. The most long-lasting treatments are a chemical peel, laser therapy, and microneedling. These all work in slightly different ways, but their main goal is to stimulate the production of new, unpigmented skin cells to even out your skin tone. Still, it’s always possible the melasma will come back after a while.
Topical creams like retinol and retinoids can also bring about animprovement in your melasma (and as a bonus, they’re a great acne treatment!), but they’re only effective while you’re using them. After you stop, your skin might become pigmented again.
If you’re suffering from dermal melasma, there are even fewer long-term treatment options. That’s because this pigment is in the deeper layers of skin, meaning surface laser treatment and chemical peels can’t reach them. Your best bet in these cases might be prescription cream like hydroquinone.
How Do You Stop Melasma From Spreading?
The biggest thing you can do to stop melasma from getting worse is to limit your sun exposure. Always use an SPF when going outside, and if you have to be in the sun, try to find shade or wear a hat.
Other than reducing sun exposure, make sure to use your treatment as prescribed. Keep your skin healthy and hydrated by moisturizing twice a day. Additionally, use only gentle and non-abrasive soaps and cleansers on the face to avoid irritating your skin.
Preventing Melasma
Since melasma is often caused by excess hormones, there’s not a lot you can always do to prevent it. In the case of melasma caused by pregnancy hormones, it may just be something you have to deal with. However, there are a few ways you may be able to alter your lifestyle to stop melasma.
How Can You Naturally Prevent Melasma?
If you’re looking for home remedies for melasma, we’ve got bad news. Science has generally proven that melasma doesn’t respond to at-home treatments like lemon juice or aloe vera. Instead, a better option might be to find what’s causing your melasma and address that. For example, if you’re on estrogen birth control, you might ask your medical provider if you can switch to a non-hormonal birth control instead.
And like we’ve said multiple times before, sun protection is crucial. Limit sun exposure and add an SPF to your skincare routine to reduce skin discoloration.
What Vitamins Are Good for Preventing Melasma?
Unfortunately, science hasn’t found a direct link between specific vitamin intake and melasma. That said, eating a healthy and well-balanced diet is crucial for overall skin health. You can also use some vitamins topically on your skin.
Vitamin C is an especially important one, as it helps to promote collagen production and inhibit melanin production. Vitamin A is another skin care product that can be helpful, as it controls the levels of tyrosinase in the skin. Tyrosinase is an enzyme that contributes to melanin production.
When Should Someone Begin Trying to Prevent Melasma?
Melasma isn’t something you should necessarily try to prevent at a specific point, especially since it’s usually caused by factors outside of your control. Rather, a better idea is to just take good care of your skin. This should limit your chances of all skin conditions. Use a regimen of cleansers, creams, and moisturizers daily to keep your skin fresh and hydrated.
If you think you might be experiencing melasma and want to know what your treatment options are, get started here by filling out a skincare questionnaire.